Retractable Grounding Assembly: Design and Applications
Retractable Grounding Assembly: Design and Applications

Abstract
A retractable grounding assembly is an essential component in electrical and mechanical systems where temporary or adjustable grounding is required. This article discusses the design principles, working mechanisms, and key applications of retractable grounding assemblies in industries such as aerospace, power distribution, and telecommunications.
1. Introduction
Grounding is critical for electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and static discharge prevention. A retractable grounding assembly provides a flexible solution, allowing grounding connections to be engaged or disengaged as needed. These systems are particularly useful in dynamic environments where permanent grounding is impractical.
2. Design and Components
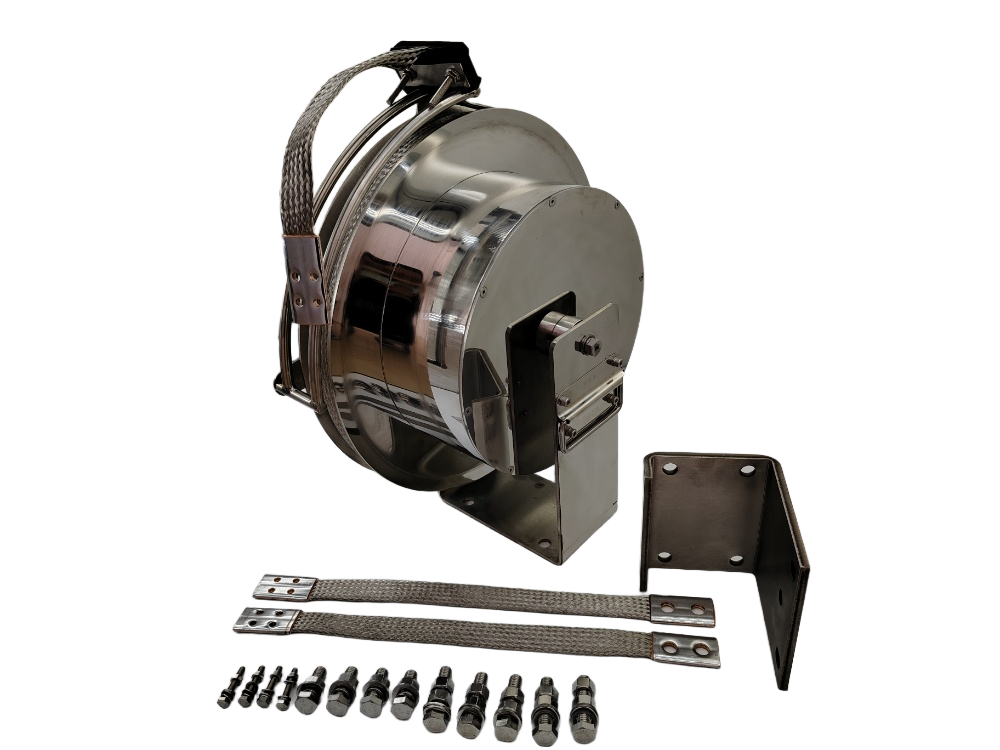
A typical retractable grounding assembly consists of the following components:
Conductive Cable/Braid: Flexible, high-conductivity material (e.g., copper, tinned copper, or stainless steel).
Retraction Mechanism: Spring-loaded or motorized system for extension and retraction.
Contact Terminal: Ensures a low-resistance connection to the grounding point.
Housing Unit: Protects internal components from environmental factors (moisture, dust, etc.).
Locking Mechanism: Secures the assembly in extended or retracted positions.
3. Working Principle
The retractable grounding assembly operates in two primary modes:
Extended (Engaged) Mode: The conductive element makes direct contact with the grounding surface, providing a safe path for electrical discharge.
Retracted (Disengaged) Mode: The grounding element withdraws into the housing, preventing unnecessary wear or interference.
Automated versions may use sensors to detect when grounding is required (e.g., during aircraft refueling or high-voltage equipment maintenance).
4. Applications
4.1 Aerospace Industry
Used in aircraft fueling systems to prevent static sparks.
Retractable grounding probes in satellites and spacecraft.
4.2 Power Systems
Temporary grounding for maintenance of high-voltage power lines.
Switchgear and transformer grounding in substations.
4.3 Industrial and Telecommunications
Grounding for mobile equipment and machinery.
ESD (electrostatic discharge) protection in sensitive electronic manufacturing.
5. Advantages
Flexibility: Adjustable length and positioning.
Durability: Resistant to mechanical stress and corrosion.
Safety: Prevents accidental contact when not in use.
Automation Compatibility: Can be integrated with control systems.
6. Challenges and Considerations
Contact Resistance: Must maintain low resistance for effective grounding.
Mechanical Wear: Frequent extension/retraction cycles may degrade components.
Environmental Factors: Moisture, temperature, and chemical exposure can affect performance.
7. Conclusion
Retractable grounding assemblies offer a reliable and adaptable solution for dynamic grounding requirements. Advances in materials and automation are further enhancing their efficiency in critical applications. Future developments may include smart grounding systems with real-time monitoring capabilities.
References
(Include relevant standards, patents, or technical manuals depending on the focus.)